AI Under Scrutiny
09/07/2024Investment Banking,Artificial Intelligence,Change Leadership,Data & Analytics,Risk Management,Insurance,StrategyArticle
Why AI risk & governance should be a focus area for financial services firms
Introduction
As financial services firms increasingly integrate artificial intelligence (AI) into their operations, the imperative to focus on AI risk & governance becomes paramount. AI offers transformative potential, driving innovation, enhancing customer experiences, and streamlining operations. However, with this potential comes significant risks that can undermine the stability, integrity, and reputation of financial institutions. This article delves into the critical importance of AI risk & governance for financial services firms, providing a detailed exploration of the associated risks, regulatory landscape, and practical steps for effective implementation. Our goal is to persuade financial services firms to prioritise AI governance to safeguard their operations and ensure regulatory compliance.
The Growing Role of AI in Financial Services
AI adoption in the financial services industry is accelerating, driven by its ability to analyse vast amounts of data, automate complex processes, and provide actionable insights. Financial institutions leverage AI for various applications, including fraud detection, credit scoring, risk management, customer service, and algorithmic trading. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, AI could potentially generate up to $1 trillion of additional value annually for the global banking sector.
Applications of AI in Financial Services
1 Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI algorithms analyse transaction patterns to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, reducing losses and enhancing security.
2 Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment: AI models evaluate creditworthiness by analysing non-traditional data sources, improving accuracy and inclusivity in lending decisions.
3 Customer Service and Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer support, while machine learning algorithms offer personalised product recommendations.
4 Personalised Financial Planning: AI-driven platforms offer tailored financial advice and investment strategies based on individual customer profiles, goals, and preferences, enhancing client engagement and satisfaction.
Potential Benefits of AI
The benefits of AI in financial services are manifold, including increased efficiency, cost savings, enhanced decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction. AI-driven automation reduces manual workloads, enabling employees to focus on higher-value tasks. Additionally, AI's ability to uncover hidden patterns in data leads to more informed and timely decisions, driving competitive advantage.
The Importance of AI Governance
AI governance encompasses the frameworks, policies, and practices that ensure the ethical, transparent, and accountable use of AI technologies. It is crucial for managing AI risks and maintaining stakeholder trust. Without robust governance, financial services firms risk facing adverse outcomes such as biased decision-making, regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Key Components of AI Governance
1 Ethical Guidelines: Establishing ethical principles to guide AI development and deployment, ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency.
2 Risk Management: Implementing processes to identify, assess, and mitigate AI-related risks, including bias, security vulnerabilities, and operational failures.
3 Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to relevant laws and regulations governing AI usage, such as data protection and automated decision-making.
4 Transparency and Accountability: Promoting transparency in AI decision-making processes and holding individuals and teams accountable for AI outcomes.
Risks of Neglecting AI Governance
Neglecting AI governance can lead to several significant risks:
1 Embedded bias: AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate biases if trained on biased data or if developers inadvertently incorporate them. This can lead to unfair treatment of certain groups and potential violations of fair lending laws.
2 Explainability and complexity: AI models can be highly complex, making it challenging to understand how they arrive at decisions. This lack of explainability raises concerns about transparency, accountability, and regulatory compliance
3 Cybersecurity: Increased reliance on AI systems raises cybersecurity concerns, as hackers may exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms or systems to gain unauthorised access to sensitive financial data
4 Data privacy: AI systems rely on vast amounts of data, raising privacy concerns related to the collection, storage, and use of personal information
5 Robustness: AI systems may not perform optimally in certain situations and are susceptible to errors. Adversarial attacks can compromise their reliability and trustworthiness
6 Impact on financial stability: Widespread adoption of AI in the financial sector can have implications for financial stability, potentially amplifying market dynamics and leading to increased volatility or systemic risks
7 Underlying data risks: AI models are only as good as the data that supports them. Incorrect or biased data can lead to inaccurate outputs and decisions
8 Ethical considerations: The potential displacement of certain roles due to AI automation raises ethical concerns about societal implications and firms' responsibilities to their employees
9 Regulatory compliance: As AI becomes more integral to financial services, there is an increasing need for transparency and regulatory explainability in AI decisions to maintain compliance with evolving standards
10 Model risk: The complexity and evolving nature of AI technologies mean that their strengths and weaknesses are not yet fully understood, potentially leading to unforeseen pitfalls in the future
To address these risks, financial institutions need to implement robust risk management frameworks, enhance data governance, develop AI-ready infrastructure, increase transparency, and stay updated on evolving regulations specific to AI in financial services.
The consequences of inadequate AI governance can be severe. Financial institutions that fail to implement proper risk management and governance frameworks may face significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and regulatory scrutiny. The proposed EU AI Act, for instance, outlines fines of up to €30 million or 6% of global annual turnover for non-compliance. Beyond regulatory consequences, poor AI governance can lead to biased decision-making, privacy breaches, and erosion of customer trust, all of which can have long-lasting impacts on a firm's operations and market position.
Regulatory Requirements
The regulatory landscape for AI in financial services is evolving rapidly, with regulators worldwide introducing guidelines and standards to ensure the responsible use of AI. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a critical component of building a sustainable and trustworthy AI strategy.
Key Regulatory Frameworks
1 General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The European Union's GDPR imposes strict requirements on data processing and the use of automated decision-making systems, ensuring transparency and accountability.
2 Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): The FCA in the UK has issued guidance on AI and machine learning, emphasising the need for transparency, accountability, and risk management in AI applications.
3 Federal Reserve: The Federal Reserve in the US has provided supervisory guidance on model risk management, highlighting the importance of robust governance and oversight for AI models.
4 Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): MAS has introduced guidelines for the ethical use of AI and data analytics in financial services, promoting fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency (FEAT).
5 EU AI Act: This new act aims to protect fundamental rights, democracy, the rule of law and environmental sustainability from high-risk AI, while boosting innovation and establishing Europe as a leader in the field. The regulation establishes obligations for AI based on its potential risks and level of impact.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for several reasons:
1 Legal Obligation: Financial services firms must adhere to laws and regulations governing AI usage to avoid legal penalties and fines.
2 Reputational Risk: Non-compliance can damage a firm's reputation, eroding trust with customers, investors, and regulators.
3 Operational Efficiency: Regulatory compliance ensures that AI systems are designed and operated according to best practices, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.
4 Stakeholder Trust: Adhering to regulatory standards builds trust with stakeholders, demonstrating a commitment to responsible and ethical AI use.
Identifying AI Risks
AI technologies pose several specific risks to financial services firms that must be identified and mitigated through effective governance frameworks.
Bias and Discrimination
AI systems can reflect and reinforce biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For instance, biased credit scoring models may disadvantage certain demographic groups, resulting in unequal access to financial services. Addressing bias requires rigorous data governance practices, including diverse and representative training data, regular bias audits, and transparent decision-making processes.
Security Risks
AI systems are vulnerable to various security threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and adversarial manipulations. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in AI models to manipulate outcomes or gain unauthorised access to sensitive financial data. Ensuring the security and integrity of AI systems involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures, regular security assessments, and incident response plans.
Operational Risks
AI-driven processes can fail or behave unpredictably under certain conditions, potentially disrupting critical financial services. For example, algorithmic trading systems can trigger market instability if not responsibly managed. Effective governance frameworks include comprehensive testing, continuous monitoring, and contingency planning to mitigate operational risks and ensure reliable AI performance.
Compliance Risks
Failure to adhere to regulatory requirements can result in significant fines, legal consequences, and reputational damage. AI systems must be designed and operated in compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as data protection and automated decision-making guidelines. Regular compliance audits and updates to governance frameworks are essential to ensure ongoing regulatory adherence.
Benefits of Effective AI Governance
Implementing robust AI governance frameworks offers numerous benefits for financial services firms, enhancing risk management, trust, and operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation
Effective AI governance helps identify, assess, and mitigate AI-related risks, reducing the likelihood of adverse outcomes. By implementing comprehensive risk management processes, firms can proactively address potential issues and ensure the safe and responsible use of AI technologies.
Enhanced Trust and Transparency
Transparent and accountable AI practices build trust with customers, regulators, and other stakeholders. Clear communication about AI decision-making processes, ethical guidelines, and risk management practices demonstrates a commitment to responsible AI use, fostering confidence and credibility.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to governance frameworks ensures compliance with current and future regulatory requirements, minimising legal and financial repercussions. Robust governance practices align AI development and deployment with regulatory standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
Operational Efficiency
Governance frameworks streamline the development and deployment of AI systems, promoting efficiency and consistency in AI-driven operations. Standardised processes, clear roles and responsibilities, and ongoing monitoring enhance the effectiveness and reliability of AI applications, driving operational excellence.
Case Studies
Several financial services firms have successfully implemented AI governance frameworks, demonstrating the tangible benefits of proactive risk management and responsible AI use.
JP Morgan Chase
JP Morgan Chase has established a comprehensive AI governance structure that includes an AI Ethics Board, regular audits, and robust risk assessment processes. The AI Ethics Board oversees the ethical implications of AI applications, ensuring alignment with the bank's values and regulatory requirements. Regular audits and risk assessments help identify and mitigate AI-related risks, enhancing the reliability and transparency of AI systems.
ING Group
ING Group has developed an AI governance framework that emphasises transparency, accountability, and ethical considerations. The framework includes guidelines for data usage, model validation, and ongoing monitoring, ensuring that AI applications align with the bank's values and regulatory requirements. By prioritising responsible AI use, ING has built trust with stakeholders and demonstrated a commitment to ethical and transparent AI practices.
HSBC
HSBC has implemented a robust AI governance framework that focuses on ethical AI development, risk management, and regulatory compliance. The bank's AI governance framework includes a dedicated AI Ethics Committee, comprehensive risk management processes, and regular compliance audits. These measures ensure that AI applications are developed and deployed responsibly, aligning with regulatory standards and ethical guidelines.
Practical Steps for Implementation
To develop and implement effective AI governance frameworks, financial services firms should consider the following actionable steps:
Establish a Governance Framework
Develop a comprehensive AI governance framework that includes policies, procedures, and roles and responsibilities for AI oversight. The framework should outline ethical guidelines, risk management processes, and compliance requirements, providing a clear roadmap for responsible AI use.
Create an AI Ethics Board
Form an AI Ethics Board or committee to oversee the ethical implications of AI applications and ensure alignment with organisational values and regulatory requirements. The board should include representatives from diverse departments, including legal, compliance, risk management, and technology.
Implement Specific AI Risk Management Processes
Conduct regular risk assessments to identify and mitigate AI-related risks. Implement robust monitoring and auditing processes to ensure ongoing compliance and performance. Risk management processes should include bias audits, security assessments, and contingency planning to address potential operational failures.
Ensure Data Quality and Integrity
Establish data governance practices to ensure the quality, accuracy, and integrity of data used in AI systems. Address potential biases in data collection and processing, and implement measures to maintain data security and privacy. Regular data audits and validation processes are essential to ensure reliable and unbiased AI outcomes.
Invest in Training and Awareness
Provide training and resources for employees to understand AI technologies, governance practices, and their roles in ensuring ethical and responsible AI use. Ongoing education and awareness programs help build a culture of responsible AI use, promoting adherence to governance frameworks and ethical guidelines.
Engage with Regulators and Industry Bodies
Stay informed about regulatory developments and industry best practices. Engage with regulators and industry bodies to contribute to the development of AI governance standards and ensure alignment with evolving regulatory requirements. Active participation in industry forums and collaborations helps stay ahead of regulatory changes and promotes responsible AI use.
Conclusion
As financial services firms continue to embrace AI, the importance of robust AI risk & governance frameworks cannot be overstated. By proactively addressing the risks associated with AI and implementing effective governance practices, firms can unlock the full potential of AI technologies while safeguarding their operations, maintaining regulatory compliance, and building trust with stakeholders. Prioritising AI risk & governance is not just a regulatory requirement but a strategic imperative for the sustainable and ethical use of AI in financial services.
References and Further Reading
- McKinsey & Company. (2020). The AI Bank of the Future: Can Banks Meet the AI Challenge?
- European Union. (2018). General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). (2019). Guidance on the Use of AI and Machine Learning in Financial Services.
- Federal Reserve. (2020). Supervisory Guidance on Model Risk Management.
- JP Morgan Chase. (2021). AI Ethics and Governance Framework.
- ING Group. (2021). Responsible AI: Our Approach to AI Governance.
- Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). (2019). FEAT Principles for the Use of AI and Data Analytics in Financial Services.
For further reading on AI governance and risk management in financial services, consider the following resources:
- "Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Financial Services Firms" by Deloitte
- "Managing AI Risk in Financial Services" by PwC
- "AI Ethics and Governance: A Global Perspective" by the World Economic Forum
Strengthening Information Security
17/04/2024Corporate Banking,Risk Management,Data Governance,Investment Banking,Data & Analytics,Data Quality,Insurance,StrategyArticle
The Combined Power of Identity & Access Management and Data Access Controls
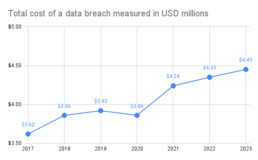
The digital age presents a double-edged sword for businesses. While technology advancements offer exciting capabilities in cloud, data analytics, and customer experience, they also introduce new security challenges. Data breaches are a constant threat, costing businesses an average of $4.45 million per incident according to a 2023 IBM report (https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach) and eroding consumer trust. Traditional security measures often fall short, leaving vulnerabilities for attackers to exploit. These attackers, targeting poorly managed identities and weak data protection, aim to disrupt operations, steal sensitive information, or even hold companies hostage. The impact extends beyond the business itself, damaging customers, stakeholders, and the broader financial market
In response to these evolving threats, the European Commission (EU) has implemented the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) (Regulation (EU) 2022/2554). This regulation focuses on strengthening information and communications technology (ICT) resilience standards in the financial services sector. While designed for the EU, DORA’s requirements offer valuable insights for businesses globally, especially those with operations in the EU or the UK. DORA mandates that financial institutions define, approve, oversee, and be accountable for implementing a robust risk-management framework. This is where identity & access management (IAM) and data access controls (DAC).
The Threat Landscape and Importance of Data Security
Data breaches are just one piece of the security puzzle. Malicious entities also employ malware, phishing attacks, and even exploit human error to gain unauthorised access to sensitive data. Regulatory compliance further emphasises the importance of data security. Frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA mandate robust data protection measures. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Organisations, in a rapidly-evolving hybrid working environment, urgently need to implement or review their information security strategy. This includes solutions that not only reduce the attack surface but also improve control over who accesses what data within the organisation. IAM and DAC, along with fine-grained access provisioning for various data formats, are critical components of a strong cybersecurity strategy.
Keep reading to learn the key differences between IAM and DAC, and how they work in tandem to create a strong security posture.
Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Think of IAM as the gatekeeper to your digital environment. It ensures only authorised users can access specific systems and resources. Here is a breakdown of its core components:
- Identity Management (authentication): This involves creating, managing, and authenticating user identities. IAM systems manage user provisioning (granting access), authentication (verifying user identity through methods like passwords or multi-factor authentication [MFA]), and authorisation (determining user permissions). Common identity management practices include:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Users can access multiple applications with a single login, improving convenience and security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):An extra layer of security requiring an additional verification factor beyond a password (e.g., fingerprint, security code).
- Passwordless: A recent usability improvement removes the use of passwords and replaces them with authentication apps and biometrics.
- Adaptive or Risk-based Authentication: Uses AI and machine learning to analyse user behaviour and adjust authentication requirements in real-time based on risk level.
- Access Management (authorisation): Once a user has had their identity authenticated, then access management checks to see what resources the user has access to. IAM systems apply tailored access policies based on user identities and other attributes. Once verified, IAM controls access to applications, data, and other resources.
Advanced IAM concepts like Privileged Access Management (PAM) focus on securing access for privileged users with high-level permissions, while Identity Governance ensures user access is reviewed and updated regularly.
Data Access Control (DAC)
While IAM focuses on user identities and overall system access, DAC takes a more granular approach, regulating access to specific data stored within those systems. Here are some common DAC models:
- Discretionary Access Control (also DAC): Allows data owners to manage access permissions for other users. While offering flexibility, it can lead to inconsistencies and security risks if not managed properly. One example of this is UNIX files, where an owner of a file can grant or deny other users access.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Here, the system enforces access based on pre-defined security labels assigned to data and users. This offers stricter control but requires careful configuration.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This approach complements IAM RBAC by defining access permissions for specific data sets based on user roles.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Permissions are granted based on a combination of user attributes, data attributes, and environmental attributes, offering a more dynamic and contextual approach.
- Encryption: Data is rendered unreadable without the appropriate decryption key, adding another layer of protection.
IAM vs. DAC: Key Differences and Working Together
While IAM and DAC serve distinct purposes, they work in harmony to create a comprehensive security posture. Here is a table summarising the key differences:
FEATURE
IAM
DAC
Description
Controls access to applications
Controls access to data within applications
Granularity
Broader – manages access to entire systems
More fine-grained – controls access to specific data check user attributes
Enforcement
User-based (IAM) or system-based (MAC)
System-based enforcement (MAC) or user-based (DAC)
Imagine an employee accessing customer data in a CRM system. IAM verifies their identity and grants access to the CRM application. However, DAC determines what specific customer data they can view or modify based on their role (e.g., a sales representative might have access to contact information but not financial details).
Dispelling Common Myths
Several misconceptions surround IAM and DAC. Here is why they are not entirely accurate:
- Myth 1: IAM is all I need. The most common mistake that organisations make is to conflate IAM and DAC, or worse, assume that if they have IAM, that includes DAC. Here is a hint. It does not.
- Myth 2: IAM is only needed by large enterprises. Businesses of all sizes must use IAM to secure access to their applications and ensure compliance. Scalable IAM solutions are readily available.
- Myth 3: More IAM tools equal better security. A layered approach is crucial. Implementing too many overlapping IAM tools can create complexity and management overhead. Focus on choosing the right tools that complement each other and address specific security needs.
- Myth 4: Data access control is enough for complete security. While DAC plays a vital role, it is only one piece of the puzzle. Strong IAM practices ensure authorised users are accessing systems, while DAC manages their access to specific data within those systems. A comprehensive security strategy requires both.
Tools for Effective IAM and DAC
There are various IAM and DAC solutions available, and the best choice depends on your specific needs. While Active Directory remains a popular IAM solution for Windows-based environments, it may not be ideal for complex IT infrastructures or organisations managing vast numbers of users and data access needs.
Imagine a scenario where your application has 1,000 users and holds sensitive & personal customer information for 1,000,000 customers split across ten countries and five products. Not every user should see every customer record. It might be limited to the country the user works in and the specific product they support. This is the “Principle of Least Privilege.” Applying this principle is critical to demonstrating you have appropriate data access controls.
To control access to this data, you would need to create tens of thousands of AD groups for every combination of country or countries and product or products. This is unsustainable and makes choosing AD groups to manage data access control an extremely poor choice.
The complexity of managing nested AD groups and potential integration challenges with non-Windows systems highlight the importance of carefully evaluating your specific needs when choosing IAM tools. Consider exploring cloud-based IAM platforms or Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) solutions for centralised management and streamlined access control.
Building a Strong Security Strategy
The EU’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) emphasises strong IAM practices for financial institutions and will coming into act from 17 January 2025. DORA requires financial organisations to define, approve, oversee, and be accountable for implementing robust IAM and data access controls as part of their risk management framework.
Here are some key areas where IAM and DAC can help organisations comply with DORA and protect themselves:
DORA Pillar
How IAM helps
How DAC helps
ICT risk management
- Identifies risks associated with unauthorised access/misuse
- Detects users with excessive permissions or dormant accounts
- Minimises damage from breaches by restricting access to specific data
ICT related incident reporting
- Provides audit logs for investigating breaches (user activity, login attempts, accessed resources)
- Helps identify source of attack and compromised accounts
- Helps determine scope of breach and potentially affected information
ICT third-party risk management
- Manages access for third-party vendors/partners
- Grants temporary access with limited permissions, reducing attack surface
- Restricts access for third-party vendors by limiting ability to view/modify sensitive data
Information sharing
- Permissions designated users authorised to share sensitive information
- Controls access to shared information via roles and rules
Digital operational resilience testing
- Enables testing of IAM controls to identify vulnerabilities
- Penetration testing simulates attacks to assess effectiveness of IAM controls
- Ensures data access restrictions are properly enforced and minimizes breach impact
Understanding IAM and DAC empowers you to build a robust data security strategy
Use these strategies to leverage the benefits of IAM and DAC combined:
- Recognise the difference between IAM and DAC, and how they are implemented in your organisation
- Conduct regular IAM and DAC audits to identify and address vulnerabilities
- Implement best practices like the Principle of Least Privilege (granting users only the minimum access required for their job function)
- Regularly review and update user access permissions
- Educate employees on security best practices (e.g., password hygiene, phishing awareness)
Explore different IAM and DAC solutions based on your specific organisational needs and security posture. Remember, a layered approach that combines IAM, DAC, and other security measures like encryption creates the most effective defence against data breaches and unauthorised access.
Conclusion
By leveraging the combined power of IAM and DAC, you can ensure only the right people have access to the right data at the right time. This fosters trust with stakeholders, protects your reputation, and safeguards your valuable information assets.
Helping a leading insurance provider improve their data access controls
02/04/2024Data & Analytics,InsuranceCase Study
A global insurance provider had begun migrating their legacy on-premise applications to a new data lake. With a strategic reporting solution used, it was clear that report users had access to data that they did not need to have access to.
Previous studies had identified the gaps and it was time to push forward and deliver a solution. We were engaged to define the roles and data access control business rules to support Germany, as they had specific requirements around employee name visibility. A temporary solution had been implemented but a strategic solution that unmasked employee names to those who needed to see them, was required.
We developed the rules with support from the Claims business, the Data Protection Officer, and German Works Council. We designed and built a Power BI prototype to demonstrate the rules working using attribute-based access controls (ABAC).
This prototype and the business rules have led to a further engagement to implement the solution in a real report connected to the data lake.
Top 5 Trends for MLROs in 2024
28/03/2024Corporate Banking,Investment Banking,Risk Management,Insurance,StrategyArticle
Our Financial Crime Practice Lead, Kavita Harwani, recently attended the FRC Leadership Convention at the Celtic Manor, Newport, Wales. This gave us the opportunity to engage with senior leaders in the financial risk and compliance space on the latest best practices, upcoming technology advances, and practical insights.
Criminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, driving MLROs to innovate their financial crime controls. There is never a quiet time for FRC professionals, but 2024 is proving to be exceptionally busy.
Our view on the top five trends that MLROs need to focus on is presented here.
Top 5 Trends
- Minimise costs by using technology to scan the regulatory horizon and identify impacts on your business
- Accelerating transaction monitoring & decisioning by applying AI & data analytics
- Optimising due diligence with a 360 view of the customers
- Improving operational efficiency by using machine learning to automate alert handling
- Reducing financial crime risk through training and communications programmes.
1. Regulatory Compliance and Adaptation
MLROs need to stay abreast of evolving regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements. With regulatory changes occurring frequently, MLROs must ensure their organisations are compliant with the latest anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations.
This involves scanning the regulatory horizon, updating policies, procedures, and systems to reflect regulatory updates and adapting swiftly to new compliance challenges.
2. Technology & Data Analytics
MLROs will increasingly leverage advanced technology and data analytics tools to enhance their AML capabilities.
Machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics can help identify suspicious activities more effectively, allowing MLROs to detect and prevent money laundering and financial crime quicker, at lower cost, and with higher accuracy rates.
MLROs must focus on implementing robust AML technologies and optimising data analytics strategies to improve risk detection and decision-making processes.
3. Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
MLROs should prioritise strengthening CDD processes to better understand their customers’ risk of committing financial crimes.
Enhanced due diligence is critical for high-risk customers, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs) and high net worth individuals (HNWIs).
MLROs should focus on enhancing risk-based approaches to CDD and EDD, leveraging technology and data analytics to streamline customer onboarding processes while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Transaction Monitoring and Suspicious Activity Reporting
MLROs will continue to refine transaction monitoring systems to effectively identify suspicious activities and generate accurate alerts for investigation.
MLROs should focus on optimising transaction monitoring rules and scenarios to reduce false positives and prioritise high-risk transactions for further review.
Enhanced collaboration with law enforcement agencies and financial intelligence units will be crucial for timely and accurate suspicious activity reporting. Cross-industry collaboration is an expanding route to quicker insights on bad actors and behaviours.
5. Training and Awareness Programmes
MLROs must invest in comprehensive training and awareness programs to educate employees on AML risks, obligations, and best practices.
Building a strong culture of compliance within the organisation is essential for effective AML risk management.
Additionally, MLROs must promote a proactive approach to AML compliance, encouraging employees to raise concerns and seek guidance when faced with potential AML risks.
Conclusion
The expanded use of technology and data is becoming more evident from our discussions. The latest, ever-accelerating, improvements in automation and AI has brought a new set of opportunities to transform legacy manual, people-heavy processes into streamlined, efficient, and effective anti-financial crime departments.
Leading Point has a specialist financial crime team and can help strengthen your operations and meet these challenges in 2024. Reach out to our practice lead Kavita Harwani on kavita@leadingpoint.io to discuss your needs further.
Improving data access controls at a global insurer
12/03/2024Data & Analytics,FinTech,Change Leadership,Risk Management,InsuranceTestimonials
"We approached Leading Point to support the enhancement of strategic data lake fine grained access controls capabilities. Their partnership approach working transversally across business and IT functions quickly surfaced root causes to be addressed as part of the improvement plan. Leading Point's approach to consulting services was particularly refreshing from a quality and cost stand point compared to some of the traditional players that we had consulted with before."
Head of Data Controls at Global Corporate Insurer
Helping a US broker-dealer manage its application estate using open source tools
11/03/2024Wealth Management,Risk Management,Strategy,Data & AnalyticsCase Study
Our client was a Fortune 500 US independent broker-dealer with over 17,500 financial advisors and over 1tn USD in advisory and brokerage assets. They had a large application estate with nearly 1,000 applications they had either developed, bought or acquired through mergers and takeovers. The applications were captured in ServiceNow CMDB but there was little knowledge around flows, owners, data, and batch jobs.
Additionally, the client also wanted to roll out a new data strategy. Part of this engagement with their business community was to educate and inform about the data strategy and its impact on their work.
We were asked to implement an open source enterprise architecture tool called Waltz. Waltz had been originally developed at Deutsche Bank and had recently been released as open source software under FINOS (Fintech Open Source Foundation). Waltz is not widely-known in financial services yet and we saw this as a great opportunity to demonstrate the benefits of using open source tools.
To support the data strategy rollout, the client asked if we could build a simple and clear internal website to show the new data strategy and data model. The data model would be navigable to drill-down into more detail and provide links to existing documentation.
Our approach:
With our extensive implementation experience, we put together a small, experienced, cross-border team to deploy and configure Waltz. We knew that understanding the client's data was key; what data was required, where was it, how good was its quality. Waltz uses data around:
- Organisational units - different structures depending on the viewpoint (business, technical)
- People - managerial hierarchies, roles, responsibilities
- Applications - owners, technologies, costs, licences, flows, batch jobs
- Data - hierarchies, entities, attributes, definitions, quality, owners, lineage
- Capabilities - owners, services, processes
- Change - initiatives, costs, impact
We split our work into a number of workstreams:
- Data readiness - understand what data they had, the sources, and the quality
- Data configuration - understand the relationships between the data and prepare it for Waltz
- Waltz implementation - understand the base open source version of Waltz with its limitations, gather the client requirements (like single-sign on and configurable data loaders), develop the features into Waltz, and deploy Waltz at the client
- Data strategy website - understand the audience, design website prototype options for client review, build an interactive React website for the rollout roadshows
The project was challenging because, as ever, the state of the data. There were multiple inconsistencies which hinders the use of tooling to bring order. We needed to identify those inconsistencies, see who should own them, and ensure they were resolved.
With the flexibility of an enterprise architecture tool, it was important to be clear around the specific problems we wanted to solve for the client. We identified 10+ potential use cases that we worked with the client to narrow down. Future extensions of the project enabled us to extend into these other use cases.
One such problem was around batch job documentation. The client had thousands of Word docs specifying batch jobs transferring data between internal and external applications. These documents were held in SharePoint, Confluence, and local drives. This made it difficult to find information about specific batch jobs if something went wrong, for example.
We used the applications captured in Waltz and linked them together. We developed a new data loader that could import Word docs and extract the batch job information automatically from them. This was used to populate Waltz and make this information searchable, reducing the time spent by Support teams to find out about failed jobs.
One common negative that is raised about similar applications is the effort involved to get data into the application. Waltz accelerates this by sending surveys out to crowd-source knowledge from across the organisation. We found this a great way of engaging with users and capturing their experience into Waltz.
Our results:
We were able to deploy an open source enterprise architecture tool on a client's AWS cloud within three months. This included adding new features, such as single sign-on, improving existing Waltz capabilities, like the data loaders, and defining the data standards to enable smooth data integrations with source systems.
Using Waltz showed the client the value of bringing together disparate knowledge from around the organisation into one place. It does expose data gaps, but we always see this as a benefit for the client, as any improvement in data quality yields improved business results.
Helping a UK retail bank to benchmark their ESG progress against their peers
26/02/2024Data & Analytics,Corporate Banking,Risk ManagementCase Study
Our client wanted to improve their ESG position against their competitors, based on real data. They were unsure about where to start with ESG measurement and integrating ESG philosophy into their culture and business processes.
We were asked to come up with an ESG scoring model that could use existing public data from the client's peers against their own internal reporting data. This scoring model would be used to place the client against their peers in environmental, social, and governance groups, as well as an overall rating. Our ESG expertise was recognised in identifying which ESG frameworks could support this scoring model. We were also tasked with ensuring that their ESG philosophy was aligned to their purpose.
Our approach:
We used an example of best-in-class ESG stewardship in a Tier 1 financial services firm as a demonstration of what is possible. This case study covered how ESG impacted the firm across:
- Partnerships
- Products & services
- Diversity & inclusion
- Climate change
- Governance & ESG frameworks
We created an ESG scoring model that used existing ESG frameworks, such as SASB and UN SDGs. This scoring model included 32 questions across E, S and G categories. We researched public company reports to find data and references to key ESG themes. Thresholds were used to classify metrics and create a weighted score per category.
We emphasised the importance of authenticity in embedding ESG into a firm's culture. This was demonstrated through analysis of peer behaviour and assessing ESG integration into the peers' purpose. A set of recommendations were made to increase the maturity of ESG within the client, including specific frameworks and metrics to start tracking.
Our results:
The board members at the client were able to see where they stood versus their competitors, in more detail than ever before. This detail enabled a set of specific next steps to be laid out around establishing the ESG philosophy and policy of the client, which ESG areas to prioritise, changes to the risk appetite statement to incorporate ESG risks, and making a commitment to becoming net-zero.
Helping Adjoint gain ISO 27001 information security certification to support its expansion strategy
26/02/2024Data & Analytics,FinTech,Risk ManagementCase Study
Adjoint required ISO certification to comply with legislation, across multiple jurisdictions, and increase confidence in their brand. Due to the nature of their clients (fortune 500 and international companies), a widely recognised accreditation was required. The firm's incorporation of next generation processing, such as distributed ledger technology (DLT), increased the complexity to achieve certification. Their global teams in the UK, Switzerland and USA, were undergoing a heavy scaling-up.
We were asked to customise and implement an ISO 27001 framework for global accreditation in IT security management.
Our approach:
- Capture delivery requirements
- Create relevant policies, procedures and a controls framework, for applicable IT functions
- Perform gap analysis and risk assessment
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities and deliver a formal training program
- Conduct internal assurance audit to identify incidents and data breaches
- Lead external certification process with BSI, through Stage 1 and 2 completion
- Provide agile delivery through to completion
Our results:
- Effective coverage of all ISMS mandatory requirements surrounding ISO 27001
- A new performance management system to track controls in company processes, structure and focal points
- Global delivery, with clear road-mapping structure
- Scaled offerings in open APIs and raised brand in the market
- Improved sales process due to meeting client ISO requirements
Helping Adjoint, a DLT FinTech, with agile delivery management services to increase sales at pace
26/02/2024Change Leadership,FinTechCase Study
Adjoint required an experienced delivery partner to run technical delivery and build and manage client relationships, as well as create a scalable delivery model. They lacked a scalable platform and struggled to educate prospects and clients on the misconceptions between the benefits of DLT versus the noise created by other solutions.
We were asked to be the client and delivery partner, to deliver DLT solutions to fortune 50 clients, including tier 1 banks, insurers, and multinational corporations. The client wanted a scalable platform to manage internal and external work-streams, as well as internal and client resource prioritisation, to ensure better alignment of the product delivery team.
Our approach:
- Structured approach; using an Agile framework to deliver successful client PoCs and projects, whilst balancing PM, BA, Testing and DevOps deliverables
- Collaborative style; seamlessly adding capabilities and bringing delivery assets to the fore, through a low-risk delivery model, with a focus on outcomes
- Hands-on attitude; unravelling DLT, whilst enabling concrete application in treasury, captive insurance, inter-company lending, and securitisation, ensuring common messaging across clients
Our deliverables:
- Business requirements documents (BRDs)
- Testing artefacts
- Quick reference guides (QRGs)
- Support model
- Security policy
- Project plans
- Issue tracker
- Task management
Business benefits:
- Scalable, commercially attractive, and low-risk delivery model
- Optimisation of internal and external resource
- Market-ready DLT solutions with short term delivery timelines
- Recognised as an industry partner to work on value-add business use cases for DLT
- Senior stakeholder management (internal and external)
Helping a leading investment bank improve its client on-boarding processes into a single unified operating model
26/02/2024Investment Banking,Change LeadershipCase Study
Our client, like many banks, were facing multiple challenges in their onboarding and account opening processes. Scalability and efficiency were two important metrics we were asked to improve. Our senior experts interviewed the onboarding teams to document the current process and recommended a new unified process covering front, middle and back office teams.
We identified and removed key-person dependencies and documented the new process into a key operating manual for global use.
Helping Clarivate Analytics define a financial services (FS) go-to-market strategy for intellectual property data
26/02/2024Strategy,FinTech,Data & AnalyticsCase Study
We were asked by Clarivate to analyse their IP data and identify where it might be useful in financial services, based on our industry experience. We created and reviewed 39 use cases, interviewed 59 financial services specialists, and reviewed 150 potential partner companies.
We developed four value propositions and recommended 16 projects to execute the strategy.
Helping a global investment bank design & execute a client data governance target operating model
26/02/2024Change Leadership,Data & Analytics,Strategy,Investment BankingCase Study
Our client had a challenge to evidence control of their 2000+ client data elements. We were asked to implement a new target operating model for client data governance in six months. Our approach was to identify the core, essential data elements used by the most critical business processes and start governance for these, including data ownership and data quality.
We delivered business capability models, data governance processes, data quality rules & reporting, global support coverage for 100+ critical data elements supporting regulatory reporting and risk.
Helping a global investment bank reduce its residual risk with a target operating model
26/02/2024Risk Management,Change Leadership,Data & Analytics,Strategy,Investment BankingCase Study
Our client asked us to provide operating model design & governance expertise for its anti-financial crime (AFC) controls. We reviewed and approved the bank’s AFC target operating model using our structured approach, ensuring designs were compliant with regulations, aligned to strategy, and delivered measurable outcomes.
We delivered clear designs with capability impact maps, process models, and system & data architecture diagrams, enabling change teams to execute the AFC strategy.
Helping ARX, a cyber-security FinTech with interim COO services to scale-up their delivery
26/02/2024Strategy,Artificial Intelligence,FinTech,Change LeadershipCase Study
We were engaged by ARX to provide an interim COO as they gaining traction in the market and needed to scale their operations to support their new clients. We used our financial services delivery experience to take on UX/UI design, redesign their operational processes for scale, and be a delivery partner for their supply chain resilience solution.
Due to our efforts, ARX were able to meet their client demand with an improved product and more efficient sales & go-to-market approach.
Helping Bloomberg improve its data offering for its customers
26/02/2024Data Providers,Data & AnalyticsCase Study
Bloomberg wanted us to help review and refresh their 80,000 data terms in order to build a clear ontology of related information. We identified & prioritised the core, essential terms and designed new business rules for the data relationships. By creating a system-based approach, we could train the Bloomberg team to continue our work as BAU.
We improved the definitions, domains, and ranges to align with new ontologies, enabling their 300,000 financial services professionals to make more informed investment decisions.
Helping a Japanese investment bank to develop & execute their trading front-to-bank operating model
26/02/2024Investment Banking,Change LeadershipCase Study
Our client wanted to increase their trading efficiency by improving their data sourcing processes and resource efficiency in a multi-year programme. We analysed over 3,500 data feeds from 50 front office systems and over 100 reconciliations to determine how best to optimise their data.
Streamlining their data usage and operational processes is estimated to save them 20-30% costs over the next five years.
Helping a global consultancy define & execute its UK FinTech Strategy
26/02/2024Strategy,FinTechCase Study
Our client had developed 39 FinTech value propositions and we were asked to assess the propositions and prioritise when, and how, to go to market. We used our financial services experience and FinTech network to plan the best approach, through outreach, warm introductions, and events.
Our approach led to successful introductions with new prospect FinTechs in payments, neo-banks, and crypto firms within four months.
Helping GLEIF build out a new ISO standard for official organisational roles (ISO 5009)
26/02/2024Data Providers,Data & AnalyticsCase Study
GLEIF engaged us as financial services data experts to identify, analyse, and recommend relevant organisational roles for in-scope jurisdictions based on publicly-available laws & regulations. We looked at 12 locations in a four-week proof-of-concept, using automated document processing
Our work helped GLEIF to launch the ISO 5009 in 2022, enabling B2B verified digital signatures for individuals working in official roles. This digital verification speeds up onboarding time and increases trust.
Improving a DLT FinTech's operations enabling rapid scaling in target markets
25/02/2024Corporate Banking,FinTech,Investment Banking,Risk Management,Change LeadershipTestimonials
"Leading Point brings a top-flight management team, a reputation for quality and professionalism, and will heighten the value of [our] applications through its extensive knowledge of operations in the financial services sector."
Chief Risk Officer at DLT FinTech
Developing a GTM strategy at a large alternative data provider to break into new financial services markets
25/02/2024Data Providers,FinTech,Wealth Management,StrategyTestimonials
"Leading Point’s delivery has been head and shoulders above any other consultancy I have ever worked with."
SVP Large Alternative Data Provider
Increasing data product offerings by profiling 80k terms at a global data provider
25/02/2024Corporate Banking,Artificial Intelligence,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Data & Analytics,Data Providers,Investment BankingTestimonials
“Through domain & technical expertise Leading Point have been instrumental in the success of this project to analyse and remediate 80k industry terms. LP have developed a sustainable process, backed up by technical tools, allowing the client to continue making progress well into the future. I would have no hesitation recommending LP as a delivery partner to any firm who needs help untangling their data.”
PM at Global Market Data Provider
Catch the Multi-Cloud Wave
25/01/2024Strategy,Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,Multi-Cloud,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Insurance,CloudArticle
Charting Your Course
The digital realm is a constant current, pulling businesses towards new horizons. Today, one of the most significant tides shaping the landscape is the surge of multi-cloud adoption. But what exactly is driving this trend, and is your organisation prepared to ride the wave?
At its core, multi-cloud empowers businesses to break free from the constraints of a single cloud provider. Imagine cherry-picking the best services from different cloud vendors, like selecting the perfect teammates for a sailing crew. In 2022, 92% of firms either had or were considering a multi-cloud strategy (1). Having a strategy is one thing. Implementing it is a very different story. It takes meticulous planning and preparation. The potential of migrating from a single cloud provider to a multi-cloud environment can be huge if you are dealing with vast volumes of data. This flexibility unlocks a treasure trove of benefits.
1 Faction - The Continued Growth of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Infrastructure
Top 4 Benefits
1 Unmatched Agility
Respond to ever-changing demands with ease by scaling resources up or down. Multi-cloud lets you ditch the "one-size-fits-all" approach and tailor your cloud strategy to your specific needs, fostering innovation and efficiency
2 Resilience in the Face of the Storm
Don't let cloud downtime disrupt your operations. By distributing your workload across multiple providers, you create a safety net that ensures uninterrupted service even when one encounters an issue.
3 A World of Choice at Your Fingertips
No single cloud provider can be all things to all businesses. Multi-cloud empowers you to leverage the unique strengths of different vendors, giving you access to a diverse array of services and optimising your overall offering.
4 Future-Proofing Your Digital Journey
The tech landscape is a whirlwind of innovation. With multi-cloud, you're not tethered to a single provider's roadmap. Instead, you have the freedom to seamlessly adapt to emerging technologies and trends, ensuring you stay ahead of the curve.
Cost Meets the Cloud
Perhaps the most exciting development propelling multi-cloud adoption is the shrinking cost barrier. As cloud providers engage in fierce competition, prices are driving down, making multi-cloud solutions more accessible for businesses of all sizes. This cost optimisation, coupled with the strategic advantages mentioned earlier, makes multi-cloud an increasingly attractive proposition. However, a word of caution: While the overall trend is towards affordability, navigating the multi-cloud landscape still requires meticulous planning and cost management. Without proper controls and precise resource allocation, you risk increased expenses and potential setbacks. With increased distribution of data, comes the increased risk of data leakage. Not only must data be protected within each cloud environment, it needs to be protected across the multi-cloud. Data monitoring increases in complexity. As data needs to move between cloud solutions, there may be additional latency risks. These can be mitigated with good risk controls and monitoring.
Kicking Off Your Journey
Ditch single-provider limitations and enjoy flexibility, resilience, and a wider range of services to boost your digital transformation but remember…
Multi-cloud environments can heighten security risks.
Navigate cautiously with proper controls and expert guidance to avoid hidden expenses.
Fierce competition is lowering multi-cloud barriers.
Let Leading Point be your guide, helping you set sail on the multi-cloud journey with confidence and unlock its full potential.
The multi-cloud path isn't without its challenges, but the rewards are undeniable. At Leading Point, we're experts in helping businesses navigate the multi-cloud wave with confidence. Let us help you unlock the full potential of multi-cloud for a more resilient, flexible, and innovative future. So, is your organisation ready to catch the wave? Contact Leading Point today and start your multi-cloud journey!
AI in Insurance - Article 1 - A Catalyst for Innovation
20/12/2023Data & Analytics,Datatomic Ventures,Insurance,Change Leadership,Artificial Intelligence,Data Providers,FinTechArticle
How insurance companies can use the latest AI developments to innovate their operations
The emergence of AI
The insurance industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by the relentless advance of artificial intelligence (AI) and other disruptive technologies. A significant change in business thinking is gaining pace and Applied AI is being recognised for its potential in driving top-line growth and not merely a cost-cutting tool.
The adoption of AI is poised to reshape the insurance industry, enhancing operational efficiencies, improving decision-making, anticipating challenges, delivering innovative solutions, and transforming customer experiences.
This shift from data-driven to AI-driven operations is bringing about a paradigm shift in how insurance companies collect, analyse, and utilise data to make informed decisions and enhance customer experiences. By analysing vast amounts of data, including historical claims records, market forces, and external factors (global events like hurricanes, and regional conflicts), AI can assess risk with speed and accuracy to provide insurance companies a view of their state of play in the market.
Data vs AI approaches
This data-driven approach has enabled insurance companies to improve their underwriting accuracy, optimise pricing models, and tailor products to specific customer needs. However, the limitations of traditional data analytics methods have become increasingly apparent in recent years.
These methods often struggle to capture the complex relationships and hidden patterns within large datasets. They are also slow to adapt to rapidly-changing market conditions and emerging risks. As a result, insurance companies are increasingly turning to AI to unlock the full potential of their data and drive innovation across the industry.
AI algorithms, powered by machine learning and deep learning techniques, can process vast amounts of data far more efficiently and accurately than traditional methods. They can connect disparate datasets, identify subtle patterns, correlations & anomalies that would be difficult or impossible to detect with human analysis.
By leveraging AI, insurance companies can gain deeper insights into customer behaviour, risk factors, and market trends. This enables them to make more informed decisions about underwriting, pricing, product development, and customer service and gain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving marketplace.

Top 5 opportunities
1. Enhanced Risk Assessment
AI algorithms can analyse a broader range of data sources, including social media posts and weather patterns, to provide more accurate risk assessments. This can lead to better pricing and reduced losses.
2. Personalised Customer Experiences
AI can create personalised customer experiences, from tailored product recommendations to proactive risk mitigation guidance. This can boost customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Automated Claims Processing
AI can automate routine claims processing tasks, for example, by reviewing claims documentation and providing investigation recommendations, thus reducing manual efforts and improving efficiency. This can lead to faster claims settlements and lower operating costs.
4. Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI algorithms can identify anomalies and patterns in claims data to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. This can protect insurance companies from financial losses and reputational damage.
5. Predictive Analytics
AI can be used to anticipate future events, such as customer churn or potential fraud. This enables insurance companies to take proactive measures to prevent negative outcomes.
Adopting AI in Insurance
The adoption of AI in the insurance industry is not without its challenges. Insurance companies must address concerns about data quality, data privacy, transparency, and potential biases in AI algorithms. They must also ensure that AI is integrated seamlessly into their existing systems and processes.
Despite these challenges, AI presents immense opportunities. Insurance companies that embrace AI-driven operations will be well-positioned to gain a competitive edge, enhance customer experiences, and navigate the ever-changing risk landscape.
The shift from data-driven to AI-driven operations is a transformative force in the insurance industry. AI is not just a tool for analysing data; it is a catalyst for innovation and a driver of change. Insurance companies that harness the power of AI will be at the forefront of this transformation, shaping the future of insurance and delivering exceptional value to their customers.
Download the PDF article here.
The Consumer Duty Regulation
09/03/2023Consumer Duty,Wealth Management,Insurance,Regulation,Strategy,Risk Management,FinTechArticle
Improving outcomes with the Consumer Duty Regulation

How can buy-side retail financial firms improve consumer outcomes and the wider economy?
The FCA introduced new guidelines, rules and policies last year in 2022, comprised as the Consumer Duty Regulation, to ensure products and services are delivered at fair value to customers, as well as a better standard of care. With the recent rise of the cost-of-living crisis, consumers are struggling and are faced with difficult times ahead, including the UK economy. This Duty lays out responsibilities for Boards and senior management within firms, to implement this regulation, to not only benefit consumers, but the wider economy.
In a recent review published by the FCA in January 2023, the FCA identified key areas where firms are meeting obligations, and where areas of improvement are required. As stated in the Policy Statement PS22/9, the FCA would like to see firms make full use of the implementation period of this three-year strategy, to implement the Duty effectively, and that by October 2022, ‘firm’s boards (or equivalent management body) should have agreed their plans for implementing the Duty’ and to have evidenced this, to ‘challenge their plans to ensure they are deliverable and robust’ (Consumer Duty Implementation Plans, FCA, Jan 2023).
This review published by the FCA, helps firms understand the FCA’s expectations, and to work together with firms to ensure the Duty is implemented effectively. The review identified that firms are behind with the implementation of the Duty and need to improve their approach. Three key areas were suggested where firms can focus on for the second half of the implementation period, the first being ‘effective prioritisation of the Duty’ – in order to reduce risk of poor customer outcomes, and to prioritise the implementation plans. The second ‘embedding substantive requirements’, on how firms are over-confident on their plans, and instead should focus on the substantive requirements laid out in the Duty, and review ‘their products and services, communications and customer journeys, they identify and make the changes needed to meet the new standards’ (Consumer Duty Implementation Plans, FCA, Jan 2023). The third area of focus identified was on how firms should work together with other firms, to share information in the distribution chain, to ensure the Duty can be implemented effectively and consistently (Consumer Duty Implementation Plans, FCA, Jan 2023).

What can retail financial firms do to improve and what are the implications of not meeting the Duty requirements?
From the FCA’s recent review, it has been determined there are still many areas by which firms are falling short, which raises the risks of not meeting the Duty obligation deadlines. From the governance aspect, the FCA’s review has established that the board members and senior management teams within firms, have no clearly defined and developed plans in place, neither timings, and lack engagement. When it comes to the plans compiled by firms, the project requirements and timelines are unclear, there is a lack of detail, explanation, and evidence on the implementation of the Duty, including how a firm’s purpose, culture and values are in alignment with the Duty.
Additionally, the review identified that firms also fail to define risks, and internal/external dependencies such as resource planning, budgeting, and technology resources, including working together with third parties, which as a result may impact the implementation plans. Further, firms fail to distinguish mitigation strategies and approaches or methodologies for conducting reviews and gap analysis of products, services, communications, and customer journeys, as part of implementation of the Four Outcomes within the Duty. Firms have also failed to provide in-depth details into the types of data they will require, and how this will be tested, and used, to better understand the customer outcomes, which is another key part of the Duty requirements.
How can Leading Point help to simplify this process?
At Leading Point, our team of expert practitioners can assist the board members and senior managers within retail financial firms, to conduct more in-depth project scope and planning, gap analysis, as well as workflow strategies, and assist to define clear methodologies and approaches to implement the Duty policies and rules. We are fully-equipped to help any organisation that is looking to improve their implementation plans for meeting the Consumer Regulations, to ensure deadlines are met, whilst reducing costs, and risks, with defined mitigation strategies, and enhanced quality of consumer data. This will not only better equip firms with meeting the Duty obligations, but will help to accelerate new business growth, to ensure high-quality products and services are delivered to consumers.
Appendix and Additional Information on the Duty Regulation
What is the Consumer Duty Regulation?
The FCA introduced the Consumer Duty Regulation, and published the Finalised Guidelines FG22/5, along with the Policy Statement PS22/9 in July 2022, which is a ‘standard of care firms should give to customers in retail financial markets’ (FG22/9, p.3).
The FCA states that the purpose of the Consumer Duty (‘the Duty’) is to provide ‘a fairer basis for competition’, to help ‘boost growth and innovation’ (What firms and customers can expect from the consumer duty and other regulatory reforms, FCA (Sept, 2022)).
The Duty is comprised of three key areas: A Consumer Principle; the Cross-Cutting Rules; and the Four Outcomes (FG22/9, p.3). Each of these three key areas focus on how firms should deliver suitable products and services, as well as good outcomes to consumers.
Which firms and who will it impact?
The FG22/5 Guidelines state that the Duty applies ‘across retail financial services’, and that ‘firms should review all examples in this guidance and consider how they may be relevant to their business models and practices’ (FG22/5).
As stated in the FG22/5 Guidance, it is the firms responsibility to identify which rules and principles are applicable to their firm, and ‘what they are required to do’ (FG22/5).
What is the timeline of this Regulation?
It has been proposed for the Duty to be enforced in two-phase implementation periods, the first being by the end of July 2023, whereby the Duty will apply to new and existing products and services that remain for sale or open for renewal, and the second date is by July 2024, whereby the Duty will come fully into force, and will apply to all closed products and services (PS22/9).
The following timeline has been extracted from the Policy Statement – Implementation Timetable (PS22/9):
Implementation Period | Timeline |
Firms’ boards (or equivalent management body) should have agreed their implementation plans and be able to evidence they have scrutinised and challenged the plans to ensure they are deliverable and robust to meet the new standards. Firms should expect to be asked to share implementation plans, board papers and minutes with supervisors and be challenged on their contents. | End of October 2022 |
Manufacturers should aim to complete all the reviews necessary to meet the four outcome rules for their existing open products and services by the end of April 2023, so that they can:
• Share with distributors by the end of April 2023 the information necessary for them to meet their obligations under the Duty (e.g., in relation to the price and value, and products and service outcomes)
| End of April 2023 |
Manufacturers should: • Identify where changes need to be made to their existing open products and services to meet the Duty and implement these remedies by the end of July 2023 | End of July 2023 |
The Duty will apply to all new products and services, and all existing products and services that remain on sale or open for renewal. This gives firms 12 months to implement the new requirements on the bulk of retail financial products and services, benefiting the majority of consumers | End of July 2023 |
The Duty will come fully into force and apply to all closed products and services. This extra 12 months will help those firms with large numbers of closed products and will also help mitigate some of the wider concerns firms raised about the difficulty of applying the Duty to these products (see Chapter 3). | End of July 2024 |
How should firms implement the Consumer Duty Regulation?
According to the Guidance (FG22/5), it is a firm’s responsibility to identify which policies and rules apply and what they will be required to do (FG22/5). In addition to this, the Guidance has dedicated Chapter 10, on the Culture, Governance and Accountability that the Duty sets out for firms to give their customers. This is so that firms shift their focus on customer outcomes, and to ‘review the outcomes of their customers to ensure they are consistent with the Duty’ (PS22/9).
The Guidance (FG22/5) states the following:
- The rules require firms to ensure their strategies, governance, leadership, and people policies (including incentives at all levels) lead to good outcomes for customers. The rules also make clear that we expect customer outcomes to be a key lens for important areas, such as Risk and Internal Audit.
- A firm’s board, or equivalent governing body, should review and approve an assessment of whether the firm is delivering good outcomes for its customers which are consistent with the Duty, at least annually.
- Individual accountability and high standards of personal conduct in firms will ensure that firms are meeting their obligations under the Duty.
The Guidance (FG22/5) outlines four important drivers of culture that firms will need to ensure they deliver on from: Purpose; Leadership; People; and Governance. The Duty will also hold senior managers accountable via the Senior Managers & Certification Regime (SMCR) (FG22/5). A firm’s board will be responsible for the submission of a Board Report, which will be comprised of an assessment of whether the ‘firm is delivering good outcomes for its customers which are consistent with the Duty’ (FG22/5). Firms will also be required to monitor their outcomes, with a key focus of the Duty requiring firms to ‘assess, test, and understand’ and be able ‘to evidence the outcomes their customers are receiving’ (FG22/5), thus firms will be required to identify relevant sources of their data, to ensure they are consistent with meeting the obligations of the Duty, to their customers.
Unlocking the opportunity of vLEIs
08/02/2023LEI,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Insurance,Data & Analytics,vLEI,Risk Management,Strategy,Investment Banking,FinTech,Corporate Banking,Data ProvidersArticle
Streamlining financial services workflows with Verifiable Legal Entity Identifiers (vLEIs)
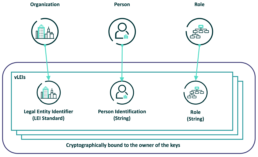
Source: GLIEF
Trust is hard to come by
How do you trust people you have never met in businesses you have never dealt with before? It was difficult 20 years ago and even more so today. Many checks are needed to verify if the person you are talking to is the person you think it is. Do they even work for the business they claim to represent? Failures of these checks manifest themselves every day with spear phishing incidents hitting the headlines, where an unsuspecting clerk is badgered into making a payment to a criminal’s account by a person claiming to be a senior manager.
With businesses increasing their cross-border business and more remote working, it is getting harder and harder to trust what you see in front of you. How do financial services firms reduce the risk of cybercrime attacks? At a corporate level, there are Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs) which have been a requirement for regulated financial services businesses to operate in capital markets, OTC derivatives, fund administration or debt issuance.
LEIs are issued by Local Operating Units (LOUs). These are bodies that are accredited by GLEIF (Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation) to issue LEIs. Examples of LOUs are the London Stock Exchange Group (LSEG) and Bloomberg. However, LEIs only work at a legal entity level for an organisation. LEIs are not used for individuals within organisations.
Establishing trust at this individual level is critical to reducing risk and establishing digital trust is key to streamlining workflows in financial services, like onboarding, trade finance, and anti-financial crime.
This is where Verifiable Legal Entity Identifiers (vLEIs) come into the picture.
What is the new vLEI initiative and how will it be used?
Put simply, vLEIs combine the organisation’s identity (the existing LEI), a person, and the role they play in the organisation into a cryptographically-signed package.
GLEIF has been working to create a fully digitised LEI service enabling instant and automated identity verification between counterparties across the globe. This drive for instant automation has been made possible by developments in blockchain technology, self-sovereign identity (SSI) and other decentralised key management platforms (Introducing the verifiable LEI (vLEI), GLEIF website).
vLEIs are secure digitally-signed credentials and a counterpart of the LEI, which is a unique 20-digit alphanumeric ISO-standardised code used to represent a single legal organisation. The vLEI cryptographically encompasses three key elements; the LEI code, the person identification string, and the role string, to form a digital credential of a vLEI. The GLEIF database and repository provides a breakdown of key information on each registered legal entity, from the registered location, the legal entity name, as well as any other key information pertaining to the registered entity or its subsidiaries, as GLEIF states this is of “principally ‘who is who’ and ‘who owns whom’”(GLEIF eBook: The vLEI: Introducing Digital I.D. for Legal Entities Everywhere, GLEIF Website).
In December 2022, GLEIF launched their first vLEI services through proof-of-concept (POC) trials, offering instant digitally verifiable credentials containing the LEI. This is to meet GLEIF’s goal to create a standardised, digitised service capable of enabling instant, automated trust between legal entities and their authorised representatives, and the counterparty legal entities and representatives with which they interact” (GLEIF eBook: The vLEI: Introducing Digital I.D. for Legal Entities Everywhere, page 2).
“The vLEI has the potential to become one of the most valuable digital credentials in the world because it is the hallmark of authenticity for a legal entity of any kind. The digital credentials created by GLEIF and documented in the vLEI Ecosystem Governance Framework can serve as a chain of trust for anyone needing to verify the legal identity of an organisation or a person officially acting on that organisation’s behalf. Using the vLEI, organisations can rely upon a digital trust infrastructure that can benefit every country, company, and consumers worldwide”,
Karla McKenna, Managing Director GLEIF Americas
This new approach for the automated verification of registered entities will benefit many organisations and businesses. It will enhance and speed up regulatory reports and filings, due diligence, e-signatures, client onboarding/KYC, business registration, as well as other wider business scenarios.
Imagine the spear phishing example in the introduction. A spoofed email will not have a valid vLEI cryptographic signature, so can be rejected (even automatically), saving potentially thousands of £.
How do I get a vLEI?
Registered financial entities can obtain a vLEI from a Qualified vLEI Issuer (QVI) organisation to benefit from instant verification, when dealing with other industries or businesses (Get a vLEI: List of Qualified vLEI Issuing Organisations, GLEIF Website).
A QVI organisation is authorised under GLEIF to register, renew or revoke vLEI credentials belonging to any financial entity. GLEIF offers a Qualification Program where organisations can apply to operate as a QVI. GLEIF maintain a list of QVIs on their website.
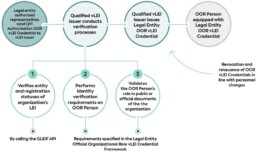
Source: GLIEF
What is the new ISO 5009:2022 and why is it relevant?
The International Organisation of Standards (ISO) published the ISO 5009 standard in 2022, which was initially proposed by GLEIF, for the financial services sector. This is a new scheme to address “the official organisation roles in a structured way in order to specify the roles of persons acting officially on behalf of an organisation or legal entity” (ISO 5009:2022, ISO.org).
Both ISO and GLEIF have created and developed this new scheme of combining organisation roles with the LEI, to enable digital identity management of credentials. This is because the ISO 5009 scheme offers a standard way to specify organisational roles in two types of LEI-based digital assets, being the public key certificates with embedded LEIs, as per X.509 (ISO/IEC 9594-8), also outlined in ISO 17442-2, or for digital verifiable credentials such as vLEIs to be specified, to help confirm the authenticity of a person’s role, who acts on behalf of an organisation (ISO 5009:2022, ISO Website). This will help speed up the validation of person(s) acting on behalf of an organisation, for regulatory requirements and reporting, as well as for ID verification, across various business use cases.
Leading Point have been supporting GLEIF in the analysis and implementation of the new ISO 5009 standard, for which GLEIF acts as the operating entity to maintain the ISO 5009 standard on behalf of ISO. Identifying and defining OORs was dependent on accurate assessments of hundreds of legal documents by Leading Point.
“We have seen first-hand the challenges of establishing identity in financial services and were proud to be asked to contribute to establishing a new standard aimed at solving this common problem. As data specialists, we continuously advocate the benefits of adopting standards. Fragmentation and trying to solve the same problem multiple times in different ways in the same organisation hurts the bottom line. Fundamentally, implementing vLEIs using ISO 5009 roles improves the customer experience, with quicker onboarding, reduced fraud risk, faster approvals, and most importantly, a higher level of trust in the business.”
Rajen Madan (Founder and CEO, Leading Point)
Thushan Kumaraswamy (Founding Partner & CTO, Leading Point)
How can Leading Point assist?
Our team of expert practitioners can assist financial entities to implement the ISO 5009 standard in their workflows for trade finance, anti-financial crime, KYC and regulatory reporting. We are fully-equipped to help any organisation that is looking to get vLEIs for their senior team and to incorporate vLEIs into their business processes, reducing costs, accelerating new business growth, and preventing anti-financial crime.
Glossary of Terms and Additional Information on GLEIF
Who is GLEIF?
The Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation (GLEIF) was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in June 2014 and as part of the G20 agenda to endorse a global LEI. The GLEIF organisation helps to implement the use of the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) and is headquartered in Basel, Switzerland.
What is an LEI?
A Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a unique 20 alphanumeric character code based on the ISO-17442 standard. This is a unique identification code for legal financial entities that are involved in financial transactions. The role of the structure of how an LEI is concatenated, principally answers ‘who is who’ and ‘who owns whom’, as per ISO and GLEIF standards, for entity verification purposes and to improve data quality in financial regulatory reports.
How does GLEIF help?
GLEIF not only helps to implement the use of LEI, but it also offers a global reference data and central repository on LEI information via the Global LEI Index on gleif.org, which is an online, public, open, standardised, and a high-quality searchable tool for LEIs, which includes both historical and current LEI records.
What is GLEIF’S Vision?
GLEIF believe that each business involved in financial transactions should be identifiable with a unique single digital global identifier. GLEIF look to increase the rate of LEI adoption globally so that the Global LEI Index can include all global financial entities that engage in financial trading activities. GLEIF believes this will encourage market participants to reduce operational costs and burdens and will offer better insight into the global financial markets (Our Vision: One Global Identity Behind Every Business, GLEIF Website).
Séverine Raymond Soulier's Interview with Leading Point
07/09/2022Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Data & Analytics,Data Providers,Strategy,Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,FinTech,Datatomic Ventures,InsuranceVideo
Séverine Raymond Soulier’s Interview with Leading Point
Séverine Raymond Soulier is the recently appointed Head of EMEA at Symphony.com – the secure, cloud-based, communication and content sharing platform. Séverine has over a decade of experience within the Investment Banking sector and following 9 years with Thomson Reuters (now Refinitiv) where she was heading the Investment and Advisory division for EMEA leading a team of senior market development managers in charge of the Investing and Advisory revenue across the region. Séverine brings a wealth of experience and expertise to Leading Point, helping expand its product portfolio and its reach across international markets.
John Macpherson's Interview with Leading Point
07/09/2022Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,Data Providers,Insurance,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Data & Analytics,Risk Management,StrategyVideo
John Macpherson’s Interview with Leading Point 2022
John Macpherson was the former CEO of BMLL Technologies; and is a veteran of the city, holding several MD roles at CITI, Nomura and Goldman Sachs. In recent years John has used his extensive expertise to advise start-ups and FinTech in challenges ranging from compliance to business growth strategy. John is Deputy Chair of the Investment Association Engine which is the trade body and industry voice for over 200+ UK investment managers and insurance companies.
Leading Point and P9 Form Collaboration to Accelerate Trade and Transaction Reporting
12/08/2022Risk Management,Transaction Reporting,Change Leadership,Data & Analytics,Trade Reporting,Investment BankingNews
Leading Point and P9 Form Collaboration to Accelerate Trade and Transaction Reporting

Leading Point and Point Nine (P9) will collaborate to streamline and accelerate the delivery of trade and transaction reporting. Together, they will streamline the delivery of trade and transaction reporting using P9’s scalable regulatory solution, and Leading Point's data management expertise. This new collaboration will help both firms better serve their clients and provide faster, more efficient reporting.
London, UK, July 22nd, 2022
P9’s in-house proprietary technology is a scalable regulatory solution. It provides best-in-class reporting solutions to both buy- and sell-side financial firms, service providers, and corporations, such as ED&F Man, FxPro and Schnigge. P9 helps them ensure high-quality and accurate trade/transaction reporting, and to remain compliant under the following regimes: EMIR, MiFIR, SFTR, FinfraG, ASIC, CFTC and Canadian.
Leading Point, a highly regarded digital transformation company headquartered in London, are specialists in intelligent data solutions. They serve a global client base of capital market institutions, market data providers and technology vendors.
Leading Point are data specialists, who have helped some of the Financial Services industry’s biggest players organise and link their data, as well as design and deliver data-led transformations in global front-to-back trading. Leading Point are experts in getting into the detail of what data is critical to businesses. They deliver automation and re-engineered processes at scale, leveraging their significant financial services domain expertise.
The collaboration will combine the power of P9's knowledge of regulatory reporting, and Leading Point’s expertise in data management and data optimisation. The integration of Leading Point’s services and P9's regulatory technology will enable clients to seamlessly integrate improved regulatory reporting and efficient business processes.
Leading Point will organise and optimise P9’s client’s data sets, making it feasible for P9's regulatory software to integrate with client regulatory workflows and reporting. In a statement made by Christina Barbash, Business Development Manager at Point Nine, she claims that, “creating a network of best-in-breed partners will enable Point Nine to better serve its existing and potential clients in the trade and transaction reporting market.”
Andreas Roussos, Partner at Point Nine adds:
“Partnering with Leading Point is a pivotal strategic move for our organization. Engaging with consulting firms will not only give us a unique position in the market, but also allow us to provide more comprehensive service to our clients, making it a game-changer for our organization, our clients, and the industry as a whole.”
Dishang Patel, COO and Founding Partner at Leading Point, speaks on the collaboration:
“We are thrilled to announce that we are collaborating with Point Nine. Their technology and knowledge of regulatory reporting can assist the wider European market. The new collaboration will unlock doors to entirely new transformation possibilities for organisations within the Financial Sector across EMEA.”
The collaboration reflects the growing complexity of financial trading and businesses’ need for more automation for compliance with regulations, whilst ensuring data management is front and centre of the approach for optimum client success. Considering this, the two firms have declared to support organisations to improve the quality and accuracy of their regulatory reporting for all regimes.
About Leading Point
Leading Point is a digital transformation company with offices in London and Dubai. They are revolutionising the way change is done through their blend of expert services and their proprietary technology, modellr™.
Find out more at: www.leadingpoint.io
Contact Dishang Patel, Founding Partner & COO at Leading Point - dishang@leadingpoint.io
About Point Nine
Point Nine (Limassol, Cyprus), is a dedicated regulatory reporting firm, focusing on the provision of trade and transaction reporting services to legal entities across the globe. Point Nine uses its in-house cutting-edge proprietary technology to provide a best-in-class solution to all customers and regulatory reporting requirements.
Find out more at: www.p9dt.com
Contact Head office, Point Nine Data Trust Limited - info@p9dt.com
ESG Operating models hold the key to ESG compliance
11/08/2022Strategy,Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,ESG,Data Providers,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,FinTech,Data & Analytics,Insurance,Risk ManagementArticle
John Macpherson on ESG Risk

In my last article, I wrote about the need for an effective operating model in the handling and optimisation of data for Financial Services firms. But data is only one of several key trends amongst these firms that would benefit from a digital operating model. ESG has risen the ranks in importance, and the reporting of this has become imperative.
The Investment Association Engine Program, which I Chair, is designed to identify the most relevant pain points and key themes amongst Asset and Investment Management clients. We do this by searching out FinTech businesses that are already working on solutions to these issues. By partnering with these businesses, we can help our clients overcome their challenges and improve their operations.
While data has been an ever-present issue, ESG has risen to an equal standing of importance over the last couple of years. Different regulatory jurisdictions and expectations worldwide has left SME firms struggling to comply and implement in a new paradigm of environmental, sustainable and governance protocols.
ESG risk is different to anything we have experienced before and does not fit into neat categories such as areas like operational risk. The depth and breadth of data and models required for firms to make informed strategic decisions varies widely based on the specific issue at hand (e.g., supply chain, reputation, climate change goals, etc.). Firms need to carefully consider their own position and objectives when determining how much analysis is needed.
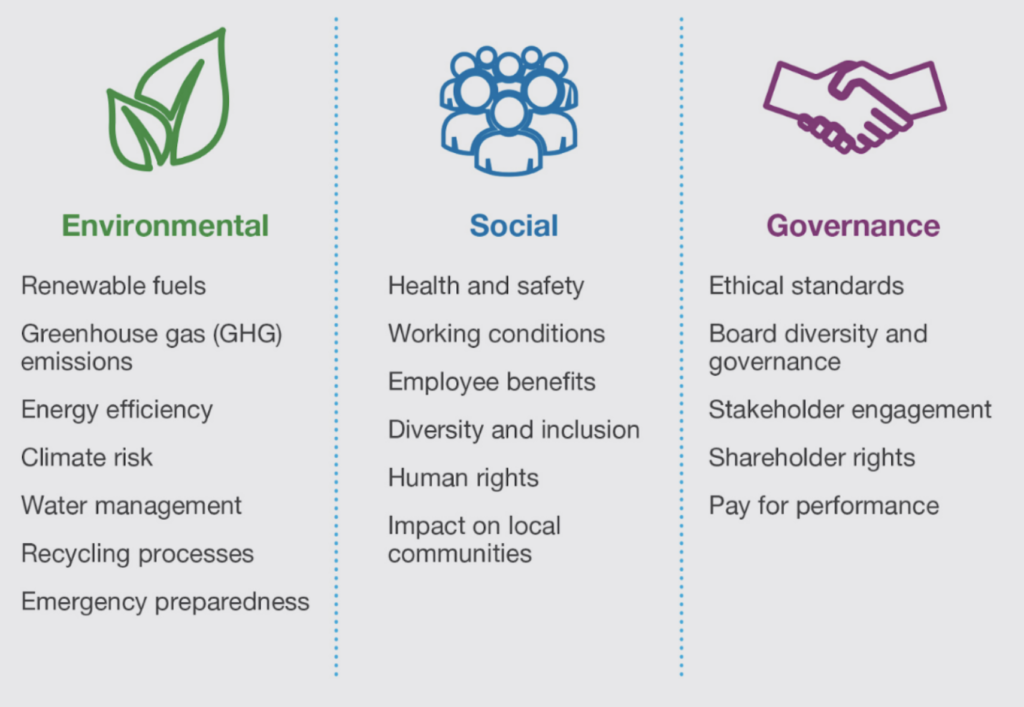
According to S&P Global, sustainable debt issuance reached a record level in 2021, and is only expected to increase further in the coming years. With this growth comes increased scrutiny and a heightened concern of so-called ‘greenwashing’, where companies falsely claim to be environmentally friendly. To combat this, participants need to manage that growth in a way that combats rising concerns about ‘greenwashing’.
Investors, regulators and the public, in general, are keen to challenge large companies’ ESG goals and results. These challenges vary wildly, but the biggest seen on a regular basis range from human rights to social unrest and climate change. As organisations begin to decarbonise their operations, they face the initially overlooked challenge of creating a credible near-term plan that will enable them to reach their long-term sustainability goals.
Investor pressure on climate change has historically focussed on the Energy sector. Now central banks are trying to incorporate climate risk as a stress testing feature for all Financial Services firms.
Source: S&P Global
Operating models hold the key to ESG transition and compliance. Having an operating model for how each of the firm’s functions intersect with ESG, requires new processes, new data, and new reporting techniques. This needs to be pulled across the enterprise, so firms have a process that is substantiated.
Before firms worry about ESG scores from their market data providers, they would do well to look closely at their own operating model and framework. In this way, they can then pull in the data required from the marketplace and use it in anger.
Leading Point is a FinTech business I am proud to be supporting. Their operating model system, modellr™ describes how financial services businesses work, from the products and services offered, to the key processes, people, data, and technology used to deliver value to their customers. This digital representation of how the business works is crucial to show what areas ESG will impact and how the firm can adapt in the most effective way.
Rajen Madan, CEO at Leading Point:
“In many ways, the transition to ESG is exposing the acute gap in firms of not being able to have meaningful dialogue with the plethora of data they already have, and need, to further add to for ESG”.
modellr™ harvests a company’s existing data to create a living dashboard, whilst also digitising the change process and enabling quicker and smarter decision-making. Access to all the information, from internal and external sources, in real time is proving transformative for SME size businesses.
Thushan Kumaraswamy, Chief Solutions Officer at Leading Point:
“ESG is already one of the biggest drivers of transformation in financial services and is only going to get bigger. Firms need to identify the impact on their business, choose the right change option, execute the strategy, and measure the improvements. The mass of ESG frameworks adds to the confusion of what to report and how. Tools such as modellr™ bring clarity and purpose to the ESG imperative.”
While most firms will look to sustainability officers for guidance on matters around ESG, Leading Point are providing these officers, and less qualified team members, with the tools to make informed decisions now, and in the future. We have established exactly what these firms need to succeed – a digital operating model.
Words by John Macpherson — Board advisor at Leading Point and Chair of the Investment Association Engine
The Challenges of Data Management
20/07/2022Change Leadership,Data Governance,Wealth Management,Data & Analytics,Insurance,Data Providers,Data Management,Data Quality,Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,FinTech,Artificial Intelligence,Risk ManagementArticle
John Macpherson on The Challenges of Data Management

I often get asked, what are the biggest trends impacting the Financial Services industry? Through my position as Chair of the Investment Association Engine, I have unprecedented access to the key decision-makers in the industry, as well as constant connectivity with the ever-expanding Fintech ecosystem, which has helped me stay at the cutting edge of the latest trends.
So, when I get asked, ‘what is the biggest trend that financial services will face’, for the past few years my answer has remained the same, data.
During my time as CEO of BMLL, big data rose to prominence and developed into a multi-billion-dollar problem across financial services. I remember well an early morning interview I gave to CNBC around 5 years ago, where the facts were starkly presented. Back then, data was doubling every three years globally, but at an even faster pace in financial markets.
Firms are struggling under the weight of this data
The use of data is fundamental to a company's operations, but they are finding it difficult to get a handle on this problem. The pace of this increase has left many smaller and mid-sized IM/ AM firms in a quandary. Their ability to access, manage and use multiple data sources alongside their own data, market data, and any alternative data sources, is sub-optimal at best. Most core data systems are not architected to address the volume and pace of change required, with manual reviews and inputs creating unnecessary bottlenecks. These issues, among a host of others, mean risk management systems cannot cope as a result. Modernised data core systems are imperative to solve where real-time insights are currently lost, with fragmented and slow-moving information.
Around half of all financial service data goes unmentioned and ungoverned, this “dark data” poses a security and regulatory risk, as well as a huge opportunity.
While data analytics, big data, AI, and data science are historically the key sub-trends, these have been joined by data fabric (as an industry standard), analytical ops, data democratisation, and a shift from big data to smaller and wider data.
Operating models hold the key to data management

Governance is paramount to using this data in an effective, timely, accurate and meaningful way. Operating models are the true gauge as to whether you are succeeding.
Much can be achieved with the relatively modest budget and resources firms have, provided they invest in the best operating models around their data.
Leading Point is a firm I have been getting to know over several years now. Their data intelligence platform modellr™, is the first truly digital operating model. modellr™ harvests a company’s existing data to create a living operating model, digitising the change process, and enabling quicker, smarter, decision making. By digitising the process, they’re removing the historically slow and laborious consultative approach. Access to all the information in real-time is proving transformative for smaller and medium-sized businesses.
True transparency around your data, understanding it and its consumption, and then enabling data products to support internal and external use cases, is very much available.
Different firms are at very different places on their maturity curve. Longer-term investment in data architecture, be it data fabric or data mesh, will provide the technical backbone to harvest ML/ AI and analytics.
Taking control of your data
Recently I was talking to a large investment bank for whom Leading Point had been brought in to help. The bank was looking to transform its client data management and associated regulatory processes such as KYC, and Anti-financial crime.
They were investing heavily in sourcing, validating, normalising, remediating, and distributing over 2,000 data attributes. This was costing the bank a huge amount of time, money, and resources. But, despite the changes, their environment and change processes had become too complicated to have any chance of success. The process results were haphazard, with poor controls and no understanding of the results missing.
Leading Point was brought in to help and decided on a data minimisation approach. They profiled and analysed the data, despite working across regions and divisions. Quickly, 2,000 data attributes were narrowed to less than 200 critical ones for the consuming functions. This allowed the financial institutions, regulatory, and reporting processes to come to life, with clear data quality measurement and ownership processes. It allowed the financial institutions to significantly reduce the complexity of their data and its usability, meaning that multiple business owners were able to produce rapid and tangible results
I was speaking to Rajen Madan, the CEO of Leading Point, and we agreed that in a world of ever-growing data, data minimisation is often key to maximising success with data!
Elsewhere, Leading Point has seen benefits unlocked from unifying data models, and working on ontologies, standards, and taxonomies. Their platform, modellr™is enabling many firms to link their data, define common aggregations, and support knowledge graph initiatives allowing firms to deliver more timely, accurate and complete reporting, as well as insights on their business processes.
The need for agile, scalable, secure, and resilient tech infrastructure is more imperative than ever. Firms’ own legacy ways of handling this data are singularly the biggest barrier to their growth and technological innovation.
If you see a digital operating model as anything other than a must-have, then you are missing out. It’s time for a serious re-think.
Words by John Macpherson — Board advisor at Leading Point, Chair of the Investment Association Engine
John was recently interviewed about his role at Leading Point, and the key trends he sees affecting the financial services industry. Watch his interview here
International Women's Day 2022
International Women’s Day 2022
![]() Presented under the theme ‘Time to break the bias’, the discussion this year focuses on the structural gender biases and stereotypes that permeate our working norms, affecting our working environment and workplace interactions – from our hiring processes to our everyday experiences.
Presented under the theme ‘Time to break the bias’, the discussion this year focuses on the structural gender biases and stereotypes that permeate our working norms, affecting our working environment and workplace interactions – from our hiring processes to our everyday experiences.
We possess a strong female presence in our company, with employees of all different ages, different races, and different stages in their careers. 3/7 of the senior management team are female, and 52% of our total employees are female.
Above, explore how the women and men of Leading Point try and break the bias in their everyday work-life. This could be striving to share your ideas up in a room full of people who don’t seem to value your opinion, or standing up for yourself when you feel patronised. This list goes on, and as women, there is nobody better to explain the shoes we walk in, but us!
Check out the full post on our instagram: https://www.instagram.com/p/Ca1-emvtH9_/?igshid=NWRhNmQxMjQ=
Leading Point Shortlisted For Data Management Insight Awards
13/01/2022Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,Data Providers,FinTech,Change Leadership,Wealth Management,Data & Analytics,Risk Management,InsuranceNews
Leading Point has been shortlisted for the A-Teams Data Management Insight Awards.
Data Management Insight Awards, now in their seventh year, are designed to recognise leading providers of data management solutions, services and consultancy within capital markets.
Leading Point has been nominated for four categories:
- Most Innovative Data Management Provider
- Best Data Analytics Solution Provider
- Best Proposition for AI, Machine Learning, Data Science
- Best Consultancy in Data Management
Areas of Outstanding Service & Innovation
Leading Form Index: Data readiness assessment, created by Leading Point FM, which measures firms data capabilities and their capacity to transform across 24 unique areas. This allows participating firms to understand the maturity of their information assets, the potential to apply new tech (AI, DLT) and benchmark with peers.
Chief Risk Officer Dashboard: Management Information Dashboard that specifies, quantifies, and visualises risks arising from firms’ non-financial, operational, fraud, financial crime, and cyber risks.
Leading Point FM ‘Think Fast’ Application: The application provides the ability to input use cases and solution journeys and helps visualise process, systems and data flows, as well as target state definition & KPI’s. This allows business change and technology teams to quickly define and initiate change management.
Anti-Financial Crime Solution: Data centric approach combined with Artificial Intelligence technology reimagines and optimises AML processes to reduce volumes of client due diligence, reduce overall risk exposure, and provide the roadmap to AI-assisted automation.
Treasury Optimisation Solution: Data content expertise leveraging cutting edge DLT & Smart Contract technology to bridge intracompany data silos and enable global corporates to access liquidity and efficiently manage finance operations.
Digital Repapering Solution: Data centric approach to sourcing, management and distribution of unstructured data combined with NLP technology to provide roadmap towards AI assisted repapering and automated contract storage and distribution.
Leading Form Practical Business Design Canvas: A practical business design method to describe your business goals & objectives, change projects, capabilities, operating model, and KPI’s to enable a true business-on-a-page view that is captured within hours.
ISO 27001 Certification – Delivery of Information Security Management System (ISMS) & Cyber risk mitigation with a Risk Analysis Tool
Leading Point have joined the SME Climate Commitment
21/12/2021ESG,Risk Management,StrategyNews
Leading Point have joined the SME Climate Commitment

What is The SME Climate Hub?
The SME Climate Hub is a global collection of SMEs (small-medium enterprises) that have commited to halve emissions by 2030 and become net-zero by 2050. Included in this commitment is to report on progress yearly.
The SME Climate Hub is a network that supports SMEs on this vital net-zero journey.
Why we joined:
Leading Point is pleased to announce that we have joined the UN-backed SME Climate Commitment and formally committed to being net-zero in carbon emissions by 2030 (in advance of the minimum target of 2050).
We have joined the community of UK businesses tackling climate change through the SME Climate Hub. With their support, we will understand, track, and make strategic, impactful emission reductions to achieve our target of being a net-zero business by 2030.
Leading Point is committed to having a responsible, sustainable, and transparent operating model. We are excited to collaborate with other businesses on this scheme, and implement a business climate strategy using the tools created by Normative, CDP, Business for Social Responsibility (BSR™), and the University of Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership (CISL).
We are proud to be taking the lead on climate action with the SME Climate Hub community and will be fully transparent with our progress.
Words from our Founding Partner and Chief Sustainability Officer, Thushan Kumaraswamy:
“Committing to a net-zero target is the right thing to do for the planet. It is also a bold statement for a growing startup. I want Leading Point to be at the forefront for fintechs who are making a climate change difference. As we grow, our impact on the environment naturally increases. I am excited to find the best ways to mitigate those impacts and share those findings with our peers.”
Words from our ESG Associate, Maria King:
“Climate change presents both potential risks and potential opportunities for businesses. Small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) account for 90% of business worldwide. However, only a small portion of these report on their emissions due to costs and complexity.”
Who we are:
Leading Point is a fintech specialising in digital operating models. We are revolutionising the way operating models are created and managed through our proprietary technology, modeller™, and expert services delivered by our team of specialists.
What COP26 means for Financial Services
21/12/2021Wealth Management,Risk Management,Investment Banking,Corporate Banking,Insurance,StrategyArticle
What COP26 means for Financial Services

Many have proclaimed COP26 as a failure, with funding falling short, loose wording and non-binding commitments. However, despite the doom and gloom, there was a bright spot; the UK’s finance industry.
Trillions need to be invested to achieve the 1.5 degrees target, but governments alone do not have the funds to achieve this. Alternative sources of finance must be found, and private investment needs to be encouraged on all fronts to, ‘go green’. Looking at supply-side energy alone, the IPPC estimates that up to $3.8 trillion needs to be mobilised annually to achieve the transition to net-zero by 2050.
The UK led from the front in green finance, introducing plans to become the world’s first net-zero aligned financial centre. New Treasury rules for financial institutions, listed on the London Stock Exchange, mean that companies will have to create and publish net-zero transition plans by 2023, although the full details are yet to be announced. These plans will be evaluated by a new institution, but crucially, are not mandatory. The adjudicator of the investment plans will be investors. Although some argue the regulation could be stronger, just like national climate targets, once there are institutions publishing their alignment with net-zero, there is a level of accountability that can be scrutinised and a platform for comparison which encourages competition. Anything stronger could have pushed investment firms into less-regulated exchanges.
Encouragingly, the private sector showed strong engagement, with nearly 500 global financial services firms agreeing to align $130 trillion — around 40% of the world’s financial assets — with the goals set out in the Paris Agreement, including limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
From large multinational companies, to small local businesses, the summit provided greater clarity on how climate policies and regulations will shape the future business environment. The progress made, on phasing out fossil fuel subsidies and coal investments, was a clear signal to the global market about the future viability of fossil fuels. It will now be more difficult to gain funding to expand existing or build new coal mines. Over time, this adjustment will have wider impacts on the funding of other polluting industries.
This new framework will give the private sector the confidence and certainty it needs to invest in green technology and green energy. Renewable energy is already the cheapest form of energy in 2/3 of the world. This reassurance will be crucial in driving the economies of scale we need, within the renewable energy industry.
A truly sustainable future is still a long way off. The private sector will still invest in fossil fuels, new regulations will cause challenges, and ESG remains optional; but initial signals from COP26 show that the future of the world is looking green.
By Maria King — ESG Associate at Leading Point
Who we are:
Leading Point is a fintech specialising in digital operating models. We are revolutionising the way operating models are created and managed through our proprietary technology, modellr™, and expert services delivered by our team of specialists.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
Leading Point is Highly Commended in Harrington Starr's Top 1% Workplace Awards
Leading Point is Highly Commended in Harrington Starr's Top 1% Workplace Awards

This third edition of The Financial Technologist brings you Harrington Starr's The Top 1% Workplace Awards 2021. We are proud to announce we have been highly commended in the category, ‘The Best Workplace for Change and Transformation’.
About the award:
"As we approach the end of 2021, it's time to celebrate the greats of our industry! This edition of The Financial Technologist brings you The Top 1% Workplace Awards, showcasing the most innovative and groundbreaking firms that are disrupting the FinTech space. We recognise the entire spectrum of excellence that exists in our industry, and gain exclusive insights into the traits and practices that put them at the fore of the marketplace." - Harrington Starr.
Judges words:
“Leading Point are altering how change and transformation should be done, fostering a revolutionary approach to change management. Equipping their team with the best tools and encouraging unique approaches amongst their team, Leading Point should rightly be commended for their work in pioneering excellence in the change and transformation space."
Congratulations to all of the winners and highly commended, in particular OpenFin and Amphora. It is a pleasure to be a part of a community who excels in their policies and practices, leading the way for global transformation.
Please take some time to read our feature article in The Financial Technologist, written by Nadyah Ibrahim and Dishang Patel: The four ingredients of an outstanding workplace - page 37.
Click here to download your free copy of Issue 3, featuring Leading Point: The Financial Technologist: The Top 1% Workplace Awards
Who we are:
Leading Point is a fintech specialising in digital operating models. We are revolutionising the way operating models are created and managed through our proprietary technology, modellr™, and expert services delivered by our team of specialists.
Partnership News: Aurachain & Leading Point to Drive Business Transformation in FS
Partnership News: Aurachain & Leading Point to Drive Business Transformation in FS
Words from Leading Point:
Earlier this year Aurachain and Leading Point announced a partnership. The agreement will combine Aurachain’s low-code platform and Leading Point’s experience with digital operating models in the fintech sector, to introduce a brand-new set of strategic business transformation offerings to client organizations. As they scale, we will be working on client projects collaboratively.
Leading Point’s Founding Partner and Chief Solutions Officer, Thush Kumaraswamy comments on the partnership: “We are excited to work with Aurachain to improve the operating models of our financial services clients by delivering cutting-edge business process automation.”
— Originally published January 2021 at Aurachain.ch —
Aurachain and Leading Point will Drive Business Transformation in Financial Markets
Aurachain, provider of the leading low-code application development platform for automation of both digital process and blockchain applications, today announced a value-added partnership with the highly regarded UK digital op model company, Leading Point. The agreement will see Aurachain’s low-code platform combined with Leading Point’s pedigree as an operational change agent in the financial services sector, to introduce a brand-new set of strategic business transformation offerings to client organizations.
The new collaboration will drive further accelerated automation initiatives and unlock doors to entirely new transformation possibilities for organizations within the financial sector. The partnership will combine the power of Aurachain’s low-code platform, which has distributed ledger technology (DLT) capabilities built-in, with the strong business transformation and project management expertise of Leading Point that specializes in delivering accelerated business deliverables.
The Aurachain low-code platform will enable Leading Point customers to accelerate digital initiatives by delivering new digital process applications up to 80% faster than traditional development methods, with participation from Leading Point SMEs and delivery experts to ensure all target client architectures meet specific business requirements. Furthermore, the platform’s ability to build and deploy applications on Distributed Ledger Technology, will empower Leading Point customers to explore the potential of tokenization within their respective markets for increased liquidity of existing assets and entirely new revenue streams that can be unlocked.
About Aurachain
Aurachain is the provider of a leading low-code application development platform for automation of both digital process and blockchain applications. The platform lets you automate end-to-end processes connecting multiple systems, teams, and departments in a continuous flow optimised for efficiency.
Arx Alliance Cyber Security Newsletter #1
07/10/2021Risk ManagementArticle
Arx Alliance Cyber Security Newsletter
Originally published October 4, 2021 at ARX
Welcome to our inaugural newsletter! Thank you for taking the time to spend a few minutes with us as we discuss the world of cybersecurity and try to share interesting stories, perspectives, and news. Those who know us already will know we are a massive advocate for the ‘little guy’ and feel more needs to be done to help create visibility, transparency, and increased education for SMEs who would otherwise not be in a position to combat or even manage an ever-worsening world of cyber. Therefore, we genuinely hope this monthly sharing of information will help organisations, both small and large, better understand and therefore manage their respective landscapes when it comes to cybersecurity and supply chain risk management.
Modern day cyber attacks
Let me first begin with a question: how many companies out there (regardless of size) believe they are immune to a cyber-attack? In my humble opinion, the simple answer is a big fat zero! Size clearly does not play a role in an organisations ability to avoid attacks which has been proven time and again as some of the largest tech companies in the world have fallen victim on multiple occasions. It therefore won’t surprise many that more than 90% of industrial companies are open to cyber-attacks. Perhaps this is due to their perceived lack of industrial organisations being tech-savvy. One such (worrying) stat was that “…penetration testers gained access to the industrial control systems (ICS) networks at 75% of these companies“. Let’s also not forget, these are often large organisations who demand and work with a large network of suppliers therefore potentially resulting in a knock-on effect that no one would want to experience. Some eye-opening & eye-catching stats within which are worth a read!
There are of course plenty of preventative measures available (but as mentioned above, unfortunately not accessible for all) however, as the old adage goes look close to home first and foremost to begin addressing issues. But what does this actually mean in a practical sense?! It’s not as complicated as it might sound at first with six basic things one can do to prevent being hacked. Changing personal behaviours will not only help individuals in their usage of personal devices but also when using company infrastructure. For instance, using free to use authenticator tools by turning on two-/multi-factor authentication and using a password manager would be two great steps to get us all started.
The importance of multi-factor authentication and strong passwords seems obvious but is regularly overlooked by the masses. This helps protect data, devices, and systems from unauthorised access. There have been many examples of poor password strength being used repeatedly including the use of the same ‘weak’ passwords for most (if not all) access. Let’s not forget, hackers are continually upping their game to ensure they can access what we don’t want them to; therefore, meaning we have to continually up our game too to stay one- step ahead. A simple change in approach of regular password changes and the use of password managers to help generate random passwords would make a material difference in this line of defence.
What are sniffing attacks?
It is important the industry terminology and acronyms don’t put people off from exploring approaches and solutions to addressing cyber issues. This not only helps cut through the jargon but also results in the basic measures being put into place for what’s (at some point inevitably) to come. Sniffing attacks is one such term that is gaining prominence among cybercriminals today to steal customer data and compromise network security.
To put into perspective exactly how much cyber criminals are raising their game, it might surprise you to know that these attacks are not at all random and opportunistic as one might think. There is a whole ecosystem where hackers can actually purchase access to victims’ networks from other cybercriminal groups and initial access brokers (IABs). Attackers are so savvy they have lists based on Geography, Revenue, Sectors, and Access Type which they are explicitly looking for in terms of vulnerabilities to target. This has gone so far that its even has a mainstream and very much identifiable name: Ransomware- as-a-Service (RaaS) with pricing far outweighed by the potential of payouts.
It is therefore no surprise that the cyber security industry is combatting people burnout! The ‘defenders’ of the peace are not only inundated but often the unsung heroes as their visibility is reduced the better the job they perform. This is of course due to increased cybercriminal sophistication which in turn means things need to change with some practice changes including investing in solutions that empower these teams to detect and stop attacks. The added ability to provide non-IT jargon-based management reports would be a massive plus to these individuals in helping to facilitate decision making at the very top. This approach will in turn promote a proactive and preventative strategy rather than fire-fighting once the problem has landed on their doorstep. Some food for thought!
Prevention and education!
Words by Dishang, COO Arx Alliance, COO Leading Point
How To Sustainably Return To The Office & Incorporate ESG
23/08/2021Risk Management,ESG,StrategyArticle
How To Sustainably Return To The Office & Incorporate ESG
Freedom has engulfed the UK since the 19th of July, with restrictions and masks now being a choice, this means the penultimate move back to the office is looming, or already loomed for many of us. After a yearlong hiatus from the bustle of office life, it is time to up our ESG game. If you’re unfamiliar with ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance), there’s no better time than now to learn. More and more businesses are adopting ESG solutions in the hopes of bettering themselves, or simply, to keep up with the times. According to The Cone Communications Millennial Employee Study, 64% of millennial workers won’t take a job if the business does not have a strong corporate social responsibility (CSR) or ESG policy (1). Studies such as these reflect the traction ESG is generating, and why companies like us are so passionate about driving it.
Ways of working have fundamentally changed, and as companies navigate this, they have the chance to ensure that the environmental aspect of ESG is not only theoretical, but implemented into their everyday ways of working. SMEs are now using significantly more electricity than they need to, i.e., a small business uses an average of 15,000-25,000 kWh per year in the UK (2). To put those numbers into perspective, the average UK household consumes 3,731 kWh per year (3), and although an office accommodates more than a typical family home would, these figures are undeniably excessive.
Returning to the office after numerous COVID-19 lockdowns gives the feeling of a fresh start. We now have a chance to create a more carbon-neutral workplace that uses less energy, produces less waste, and benefits the overall welfare of staff. Cutting your office’s electricity consumption has endless benefits, from relieving the environment of greenhouse gasses and fossil fuels to reducing the costs associated with running your firm.
2021 will see a surge in policymakers taking action to manage and measure the climate crisis, but the key question is, how will you respond?
Improve your green credentials with these 3 simple steps:
1. Reduce your carbon footprint through your transport choices – take public transport, walk, or cycle. Even carpool if possible!
2. Support your local businesses – eat lunch near the office, go to local pubs after work. This reduces the energy exuded from delivery services and travel.
3. Lower your office's electricity consumption:
i) Open windows instead of using air conditioning.
ii) Minimise artificial lighting – during daylight, open blinds instead of using bulbs.
iii) Use energy-saving bulbs – switching to LEDs could save you 85% on your lighting costs according to EON (4).
iv) Install motion sensors to control lighting in certain rooms – ensures that lights are not left on needlessly.
v) Switch off computer workstations at the end of the day – reduces electricity consumption from appliances.
vi) Reduce paper wastage – print only when necessary.
vii) Consider micro-generation (small-scale production of heat and/or electricity from a low carbon source, i.e., solar panels).
viii) Book a commercial energy audit – quantify your firm's environmental impacts.
Keeping in line with the ever-changing rules, our team have slowly and recently migrated back to the office. ESG is a huge part of our service lines and overall ethos, therefore implanting green habits upon the return to the office was hugely important. ESG expert, Ziko Townsend, who has written several pieces on the importance of ESG, lets us in on how he has successfully, sustainably, returned to the office.
“I try to do the simple things. Walk as much as possible where I can, bring my own mugs for coffee and water, and try to recycle as much as I can at home and in the office.”
As you can see, there are tonnes of small ways, to make a big impact. We are in a unique situation in the work force right now that is giving us the opportunity to reset, change old habits and form new ways of everyday working. So, leave your pre-pandemic office habits in 2020, and use your new freedom to adopt some of the above suggestions upon your return to the office.
If you would like to learn more about Leading Point and how we help businesses manage change, you can reach us here.
By Nadyah Ibrahim - Marketing and Communications Executive
Severine Raymond Soulier joins the Leading Point advisory board
18/08/2021FinTech,StrategyNews
Severine Raymond Soulier joins the Leading Point advisory board

Leading Point™ are thrilled to welcome Severine Raymond Soulier as the newest member of their advisory board. Severine joins Leading Point™ to expand the product portfolio and its reach across international markets.
Severine is the recently appointed Head of EMEA at Symphony.com – the secure, cloud-based, communication and content sharing platform. Severine has over a decade of experience within the Investment Banking sector and following 9 years with Thomson Reuters (now Refinitiv) where she was heading the Investment and Advisory division for EMEA leading a team of senior market development managers in charge of the Investing and Advisory revenue across the region. Severine Raymond brings a wealth of experience and expertise to Leading Point.
Severine Raymond Soulier says: “I am delighted to join the Leading Point team, I have been truly impressed by the talents within the team and by the transformation projects they have run with key financial players so far and look forward to bringing the company to the next level. I also fully embrace the diverse and inclusive culture of Rajen’s team and I will surely be enriched by the team and hope they can benefit from my leadership in return."
Rajen Madan, Founder & CEO of Leading Point says, "We are excited to have Severine join Leading Point. She brings expertise in strategy, go-to-market and team building for global established FS firms. She has driven high growth in her current role at Symphony. Severine’s rich experience will help us expand our product portfolio and reach across international markets. Severine is passionate about helping create future female leaders and will be a great role model and mentor to our wider team.”
Who we are:
Leading Point is a fintech specialising in digital operating models. We are revolutionising the way operating models are created and managed through our proprietary technology, modellr™, and expert services delivered by our team of specialists.
Contact: rajen@leadingpoint.io
Leading Point's Guide to Change Terms
09/08/2021Strategy,Change LeadershipArticle
Leading Point's Guide to Change Terms

We at Leading Point know all too well that the business world is full of jargon. So here's our handy guide to the eight most common terms used in change management.
Op model (AKA Operating model)
A representation of how a business works. It is not an org chart or a process map. This is traditionally done in PowerPoint and Excel.
Digital op model
This often means, how your business works in a digital world.
However, at Leading Point we believe that operating models can be done differently. To us, a digital op model is a digital representation of your operating model. This means that the op model remains live, and can be updated in real time; rather than living in a rarely opened PowerPoint.
Digital transformation
Making the business work better using digital tools and processes.
Business transformation
Any kind of significant change to how the business works.
Digitisation
Turning paper documents into structured data.
Business capability
What the business does.
Capabilities are stable and rarely change.
Business process
How the business operates.
Unlike ‘business capability’, this is variable and changes frequently.
Function
Either used as another word for capability, or another word for organisation. (This is confusing, which is why we at Leading Point don't use it.)
We hope this has helped to translate some of the jargon!
If you would like to learn more about Leading Point and how we help businesses manage change, you can reach us here.